Hyperconverged Infrastructure explained
As companies continue to rely on their digital infrastructures to maintain business operations, the need for flexible, scalable, and cost-effective solutions is critical. Hyperconverged infrastructure (HCI) has emerged as a powerful and innovative technology that can simplify IT operations while reducing costs.
This article will explore the benefits of HCI and how it compares to other infrastructure frameworks. From increased flexibility and scalability to faster deployment and better data protection, we will explore the advantages that HCI can offer and its potential risks and challenges. By the end of this article, you will have a better understanding of HCI and how it can benefit your organization.
What is HCI?
HCI is a relatively new technology that combines storage, computing, and networking in a single system, thus reducing the complexity of traditional data center infrastructure. The technology consolidates all the components of a traditional IT infrastructure into a single, software-defined solution. The result is a simplified, scalable, and more flexible IT environment. HCI solutions can be used to build private clouds, virtual desktop infrastructure (VDI), and other virtualized environments.
In a hyperconverged infrastructure, storage, compute, and network resources are integrated into a single, modular system that can be easily scaled. HCI combines storage, compute, and networking resources into a single platform, which enables IT organizations to simplify their data centers and reduce operational costs. Additionally, HCI solutions provide high availability, data protection, and disaster recovery capabilities, which are critical to business continuity.
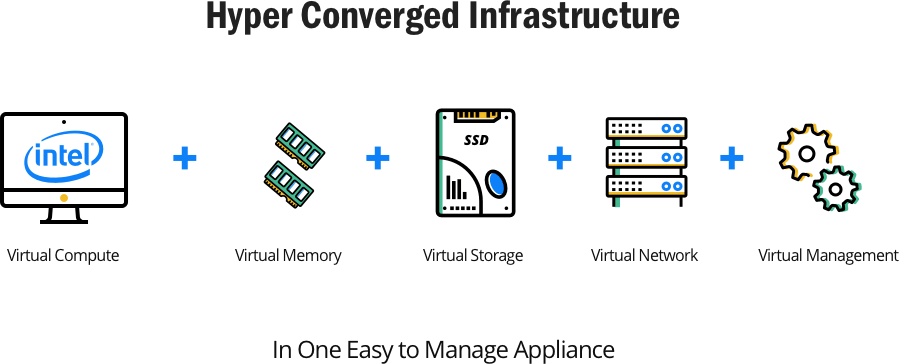
Think of it like a toolbox with all the necessary tools for a project in one place. In an HCI, all the computing resources like storage, processing power, networking, and software are combined into one compact and easy-to-use package.
This makes it simpler to manage and scale up or down as needed without adding or removing individual pieces. It’s like having a Lego set where all the blocks fit together perfectly, so you can easily build and modify your creation.
Some HCI solutions may provide the ability to scale these resources independently, while others may require scaling all resources in lockstep. In general, most HCI solutions offer some degree of flexibility in scaling, but the level of granularity may vary.
For example, some HCI solutions may allow you to add additional storage nodes to increase storage capacity without adding more compute or memory resources. In contrast, others may require you to add nodes that include compute, memory, and storage resources to scale any of these components.
Similarly, some HCI solutions may allow you to add additional network bandwidth by adding more network adapters or switches, while others may require you to add more compute or storage resources to increase network capacity.
Other requirements for HCI
HCI requires software that is installed on servers in a data center. The software is responsible for virtualizing and aggregating the servers’ compute, storage, and network resources to provide a unified, software-defined infrastructure.
Most HCI solutions provide a software package that is installed on industry-standard servers from various vendors, such as Dell, HPE, Lenovo, and others. The software is designed to work with a wide range of server hardware. However, it’s important to check with the specific HCI vendor to ensure compatibility with your chosen hardware platform.
In terms of vendors, if you want to deploy a VMWare HCI, for example, many solutions are built on top of VMWare’s vSphere visualization platform. It is common to use VMware servers in this instance. However, HCI solutions also use other virtualization platforms, such as Hyper-V or KVM, and some offer their own built-in virtualization.
An HCI can also provide the foundation for a private cloud, allowing you to create virtual machines (VMs) and deploy cloud-like services on top of the infrastructure. However, whether an HCI constitutes a private cloud depends on the specific features and capabilities of the HCI solution being used.
Some HCI solutions offer advanced cloud management and orchestration capabilities, such as self-service provisioning, automated scaling, and workload mobility, that make it easier to create and manage a private cloud. Other HCI solutions may provide more basic infrastructure services that can be used to build a private cloud but may require additional tools and processes to realize a cloud-like environment fully.
HCI vs other types of infrastructure
The main difference between hyperconverged infrastructure (HCI) and converged or non-converged infrastructure lies in how the different components of the system are integrated and managed.
In a non-converged infrastructure, the different components of the system, such as storage, processing power, and networking, are separate and managed independently. This can lead to more hardware management and software licensing complexity, as well as potential compatibility issues between different components.
The components are combined into a single system but managed separately in a converged infrastructure. This can help simplify hardware management but may require various management tools for each element.
In contrast, HCI combines all the different components of the system into a single, integrated solution. This means that storage, processing power, networking, and software are all combined into a single package and can be managed through a single interface. This can simplify hardware management and make it easier to scale the system up or down as needed.
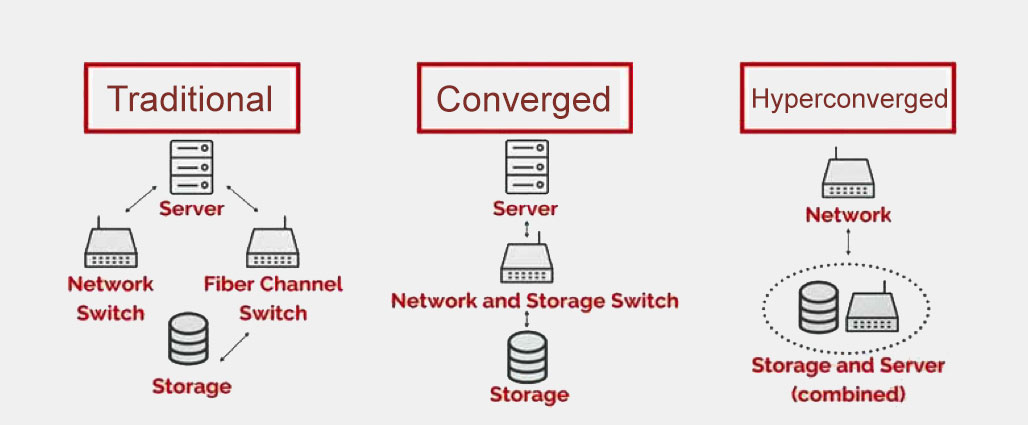
While non-converged and converged infrastructure can be effective for some businesses, HCI offers a more streamlined and flexible solution that can simplify IT operations and reduce costs.
Why adopt HCI?
There are several reasons why companies might want to adopt HCI.
- Level of integration and footprint
First, HCI can help companies reduce their data center footprint and lower the overall cost of IT infrastructure. Non-converged infrastructures typically require separate, dedicated hardware for compute, storage, and networking, often from different vendors. This can make management more complex and limit the ability to scale and quickly make changes. Additionally, non-converged infrastructure usually requires specialized expertise to manage and maintain each component, which can be costly and time-consuming.
Converged infrastructure integrates compute, storage, and networking into a single solution but typically still requires separate management of these components. This can be more streamlined than non-converged infrastructure but still falls short of the level of integration offered by HCI.
- Scalability
Second, HCI solutions are highly scalable, making adding capacity as needed easy within a single platform. Converged infrastructure combines compute, storage, and networking into a single, pre-configured solution. While CI can provide benefits such as reduced complexity and improved management, it is generally less scalable than HCI because it is designed as a fixed, pre-configured system.
In contrast, HCI is created to be highly scalable, allowing for resources to be easily added or removed as needed without requiring the purchase of pre-configured hardware units.
- Flexibility
Third, HCI solutions are more flexible than traditional data center infrastructure, allowing IT organizations to respond quickly to changing business requirements. We’ve already covered several reasons for flexibility in this article, but below is a recap.
- Simplified deployment and management: With HCI, all resources can be deployed and managed from a single interface. This simplified approach can make it easier to manage and deploy new workloads and move workloads between nodes, improving overall flexibility.
- Increased agility: HCI enables organizations to rapidly provision and scale resources as needed. This means they can easily add or remove resources in response to changing business needs, improving agility.
- Resource efficiency: HCI is designed to optimize resource utilization, which can increase flexibility. For example, storage and compute resources can be dynamically allocated based on workload demands, improving efficiency and flexibility.
- Reduced footprint: HCI can significantly reduce data center footprint, saving space, power, and cooling costs. This can make it easier to scale and deploy new resources as needed, improving overall flexibility.
- Hybrid cloud integration: Many HCI solutions integrate with public cloud platforms, allowing organizations to move workloads between their on-premises HCI infrastructure and the cloud. This can increase flexibility, enabling organizations to leverage the benefits of both on-premises and cloud resources.
- Data Protection and Disaster Recovery
Finally, HCI solutions can provide higher data protection and disaster recovery levels, which is critical for ensuring business continuity.
One advantage of HCI is its centralized management capabilities. With HCI, organizations can manage all infrastructure components from a single console, including data protection and disaster recovery features. This can simplify management, improve visibility, and reduce the risk of errors in data protection and disaster recovery workflows.
Many HCI vendors also provide integrated backup and recovery solutions that are designed to work seamlessly with the HCI platform. This integration can simplify data protection and disaster recovery processes and allow for fast recovery times in case of an outage or failure.
In addition to these benefits, HCI solutions are designed to be highly available and fault-tolerant. They provide built-in resiliency to infrastructure and application failures, helping to ensure that applications and data are available even in the event of a hardware or software failure.
Companies that deploy HCI
Several companies, including Netflix, Volkswagen, and the University of Arkansas, have successfully adopted HCI for their IT needs.
Netflix, the leading entertainment streaming service, chose to adopt HCI to improve its storage and data management capabilities. By implementing a highly scalable HCI solution, Netflix could simplify its infrastructure, reduce management overhead, and achieve greater flexibility and agility in responding to changing business needs.
The global automotive manufacturer Volkswagen implemented HCI to support its high-performance computing needs. By leveraging the flexibility and scalability of HCI, Volkswagen was able to deploy new applications and services quickly while also improving data protection and disaster recovery capabilities.
The University of Arkansas adopted HCI to modernize its IT infrastructure through VMWare and improve its data management capabilities. With HCI, the university consolidated its storage and computing resources into a single platform, simplifying management and reducing operational costs. This enabled the university to improve its services’ reliability and availability while enhancing data protection and disaster recovery capabilities.
Companies that choose HCI over other infrastructures do so because of its many benefits, including improved scalability, flexibility, reliability, and cost-effectiveness. With HCI, companies can simplify their IT infrastructure, reduce management overhead, and achieve greater agility in responding to changing business needs, making it an attractive option for many organizations.
Challenges and risks of a hyperconverged infrastructure
One challenge of HCI is complexity. With multiple components integrated into one system, it can be difficult to manage and troubleshoot when something goes wrong. Additionally, the all-in-one nature of HCI can make it more challenging to scale up or down based on changing business needs.
Another risk of HCI is data security. Since all components are combined into one system, a security breach in one area can compromise the entire system. Furthermore, the reliance on virtualization technology and shared resources can increase the risk of data theft and breaches.
HCI also requires a high level of technical expertise to deploy and manage effectively. This can be a significant challenge for smaller organizations or those with limited IT resources.
While HCI presents some challenges and risks, its streamlined management, scalability, and efficiency benefits make it a valuable option for many organizations. As with any technology implementation, it’s essential to carefully evaluate your organization’s specific needs and challenges to determine if HCI is the right fit.
Summary
In the next ten years, HCI is expected to become even more widespread as it continues to evolve to meet the changing needs of businesses. HCI will offer increased flexibility, scalability, and cost savings compared to traditional, non-converged architectures while also providing the efficiency and reliability of converged architectures.
Furthermore, the increasing adoption of cloud-based solutions and the need for cost optimization in the IT environment will bolster the appeal of HCI. HCI will provide enterprises with resources that are far more agile and scalable than traditional solutions can offer, with the flexibility to adjust quickly to changing needs and conditions.
In conclusion, with its ability to significantly reduce costs and complexity, HCI quickly becomes the preferred choice for data center infrastructure. Its scalability, flexibility, and cost-effectiveness will make it the clear choice over other non-converged and converged architectures in the next ten years.
